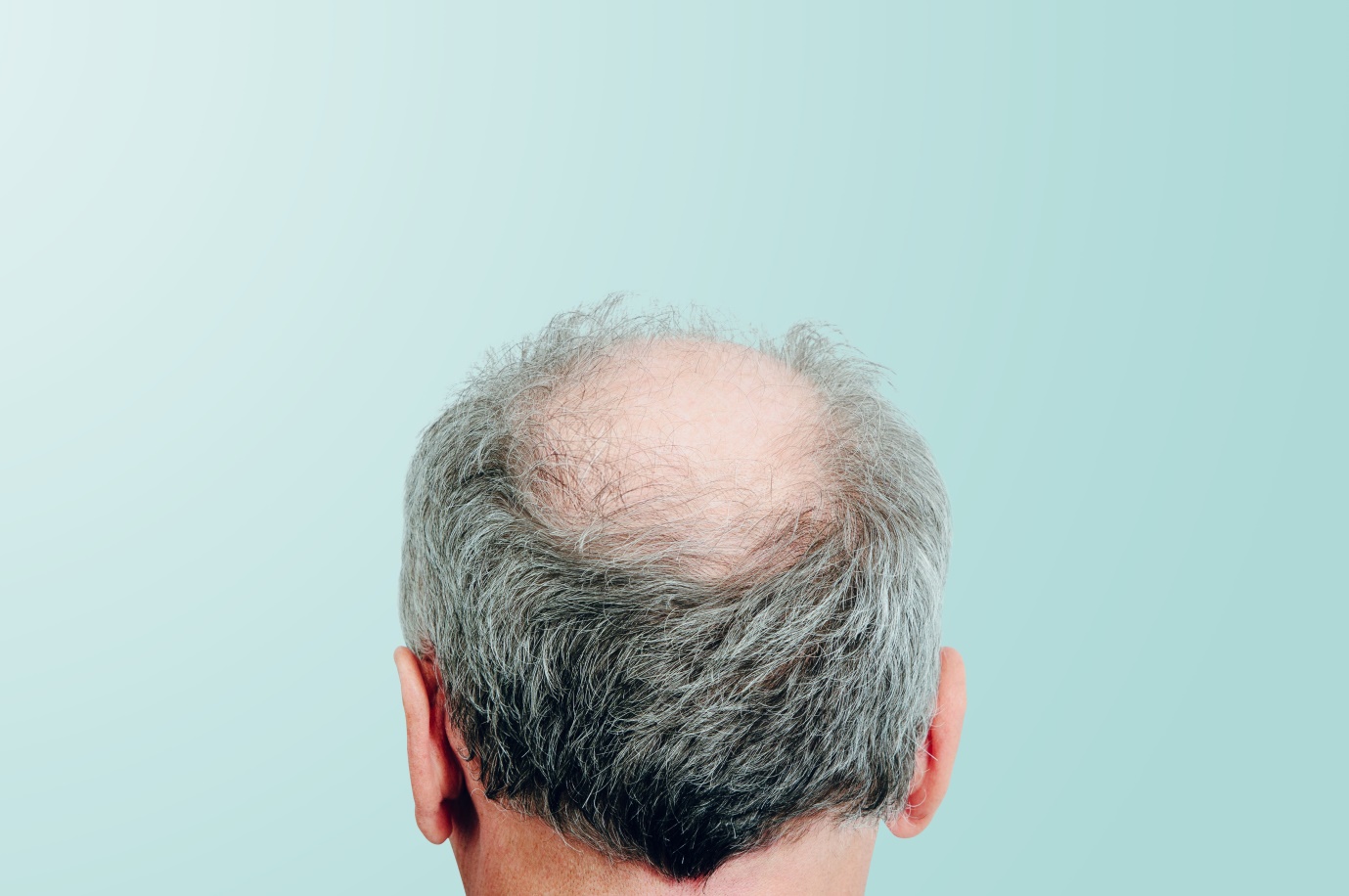
Male pattern baldness, medically known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in men. It affects over 50% of males by the age of 50 and can begin as early as the late teens or twenties. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for male pattern baldness is crucial for those looking to slow down or manage hair loss effectively.
What is Male Pattern Baldness?
Male pattern baldness is a type of hair loss that occurs in a predictable pattern, often beginning with a receding hairline and thinning hair at the crown. The condition is primarily driven by genetics and the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT binds to androgen receptors in scalp hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time—a process known as hair follicle miniaturization. Eventually, affected follicles produce finer, shorter hairs until hair growth stops altogether.
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness
The leading causes of androgenetic alopecia include:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history plays a major role
- Hormonal factors: High sensitivity to DHT and hair loss are closely linked.
- Aging: Hair follicles become more susceptible to DHT with age.
Environmental factors, stress, and poor diet can exacerbate the condition, though they are not primary causes.
Common Symptoms of Male Pattern Baldness
Early signs and symptoms include:
- Hair thinning on the temples or crown.
- Receding hairline, typically forming an “M” shape.
- Bald patches on the vertex (top of the scalp).
- Gradual hair loss over time, which may eventually lead to partial or full baldness.
Recognizing these symptoms early can increase the effectiveness of treatment.
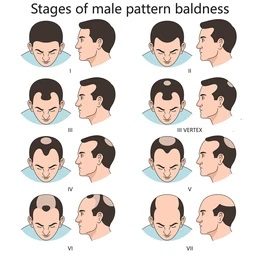
How is Male Pattern Baldness Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of male pattern baldness is usually based on:
- Clinical examination by a dermatologist.
- Patient history, including onset, progression, and family history
- In some cases, a scalp biopsy or dermoscopy and trichoscopy may be performed to rule out other causes of hair loss
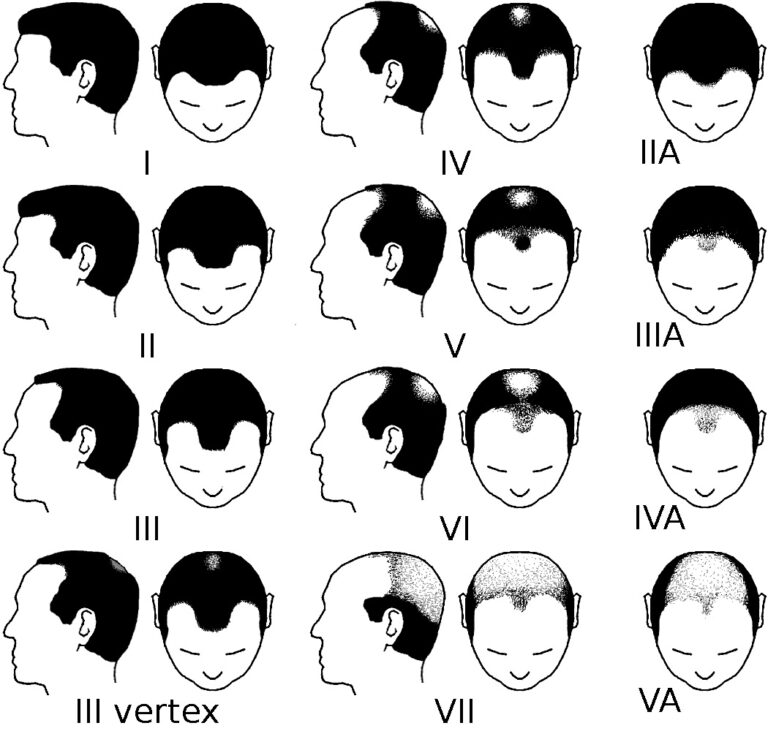
Effective Treatment Options for Male Pattern Baldness
Although male pattern baldness is not curable, several clinically approved treatments for hair loss in men can significantly slow or reverse hair thinning:
Typical diagnostic steps:
- Minoxidil (Topical):An over-the-counter solution or foam applied to the scalp. Minoxidil stimulates hair follicles and is most effective for early-stage hair loss.
- Finasteride (Oral): A prescription medication that blocks DHT production. It can prevent further hair loss and encourage regrowth, especially when started early.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive option that uses light energy to stimulate hair growth and increase follicle activity
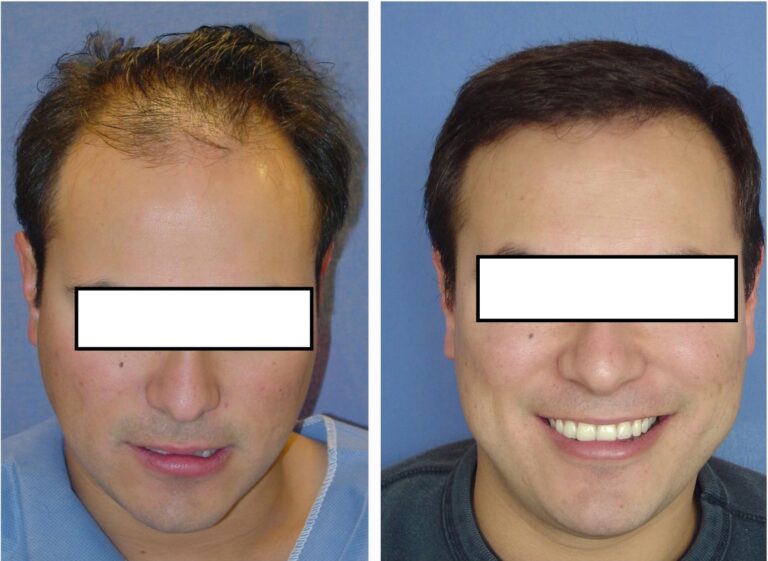
- Hair Transplantation: A surgical solution involving the transfer of healthy hair follicles from one area of the scalp to balding areas. Techniques include FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation).
Can Male Pattern Baldness Be Prevented?
While complete prevention of male pattern baldness is not currently possible due to its genetic and hormonal basis, certain measures can help reduce the rate of hair loss:
- Early treatment: Beginning medications like minoxidil or finasteride early can preserve existing hair.
- Scalp hygiene and gentle hair care: Avoid harsh chemicals, heat, and tight hairstyles.
- Healthy lifestyle: Eating a nutrient-rich diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress may support scalp health
Benefits of Treating Male Pattern Baldness
Seeking early and effective treatment can offer several advantages:
- Slows down hair loss progression
- Promotes new hair growth in thinning areas
- Boosts self-confidence by restoring a fuller, more youthful appearance
- Improves mental well-being, especially for those emotionally affected by visible hair thinning
Conclusion: Take Action Early
Male pattern baldness is a progressive condition, but early intervention and personalized treatment can make a significant difference. Whether you choose topical solutions like minoxidil, oral medications like finasteride, or more advanced options like laser therapy or hair transplant surgery, the key is to act before hair loss becomes advanced.
If you notice early signs of hair thinning or a receding hairline, consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your needs.