Hair loss in women is a common yet often distressing condition. Two of the most prevalent causes are female pattern baldness / female pattern hair loss (FPHL) (also known as female androgenetic alopecia) and telogen effluvium. Although both lead to thinning hair or excessive hair shedding, their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches differ significantly. Understanding these conditions is the first step toward effective management and hair regrowth.
What Is Female Pattern Baldness?
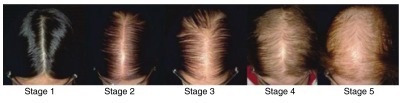
Female pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia in women, is a genetic and hormonal condition that leads to progressive hair thinning, especially at the crown and top of the scalp. Unlike male baldness, women typically retain their hairline but develop a “Christmas tree” pattern of hair loss along the central scalp.
This condition is linked to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which causes hair follicle miniaturization—a process where hair follicles shrink and produce finer, shorter hairs over time.
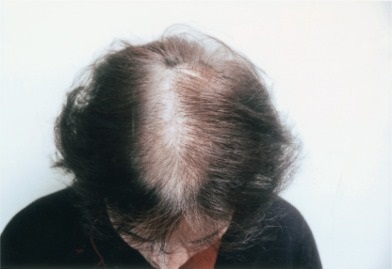
What Causes Female Pattern Baldness?
Key contributing factors include:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal imbalances, especially increased sensitivity to DHT.
- Aging, which leads to slower hair growth and thinner strands.
- Family history of androgenetic alopecia / baldness.
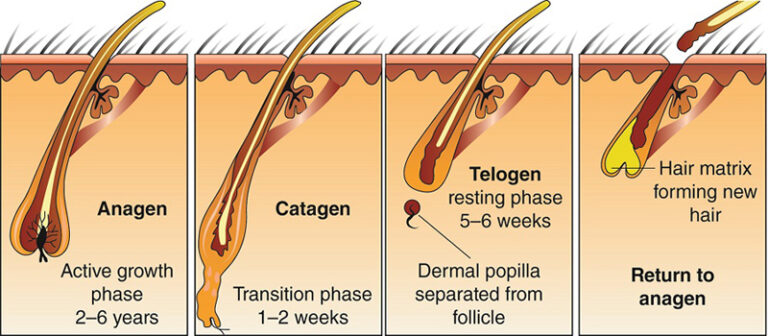
What Is Telogen Effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is a type of temporary hair loss that occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle prematurely. This results in diffuse hair shedding rather than pattern-based thinning.
Common triggers include:
- Physical or emotional stress.
- Hormonal changes (e.g., postpartum, menopause, thyroid disorders).
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as low iron, vitamin D, or protein.
- Certain medications like antidepressants, blood thinners, or beta blockers.
Symptoms of Female Pattern Baldness vs. Telogen
Effluvium
Although both conditions cause noticeable hair loss, their presentations are distinct:
Female Pattern Baldness:
- Gradual thinning hair on the top and crown of the scalp
- Wider central parting or a “Christmas tree” hair loss pattern
- Long-term progression without treatment.
Telogen Effluvium:
- Sudden, excessive hair shedding.
- Diffuse hair loss across the entire scalp.
- Clumps of hair fall out during washing or brushing.
- Usually temporary, resolving within 3–6 months after trigger correction.
Key Differences Between Female Pattern Baldness and
Telogen Effluvium
| Feature | Female Pattern Baldness | Telogen Effluvium |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Hormonal & genetic (DHT) | Stress, hormones, nutrition, medications |
| Pattern | Thinning on top/crown | Diffuse hair shedding |
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Duration | Chronic, progressive | Temporary (3–6 months) |
| Diagnosis | Scalp miniaturization | Excessive shedding, normal scalp appearance |
| Treatment | Minoxidil, hormones | Addressing the trigger, nutrition |
Diagnosis of Hair Loss in Women
Proper diagnosis is key to choosing the right treatment. A dermatologist may perform:
- Physical examination & trichoscopic evaluation of scalp.
- Medical history review (stress, medications, hormonal changes).
- Scalp biopsy (in cases of unclear diagnosis).
- Blood tests to evaluate iron levels, thyroid function, vitamin D, and hormones.
Treatment Options for Female Pattern Baldness and
Telogen Effluvium
Treatment for hair loss in women depends on the underlying cause—whether it is hormonal (androgenetic alopecia) or triggered by external factors (telogen effluvium). A comprehensive approach combining medical therapy, supportive care, and lifestyle modifications offers the best outcomes.
- Nutritional Supplements:
A well-balanced diet is essential for healthy hair growth. Specific supplements can support hair restoration, particularly in cases of telogen effluvium caused by nutritional deficiencies.- Iron, biotin, vitamin D, zinc, and protein are commonly prescribed by dermatologist.
- Best results occur when deficiencies are confirmed through blood testing.
- Recommended as part of a long-term hair health support plan.
- Topical Hair Growth Serums
Several topical formulations contain active ingredients that promote follicular activity and reduce inflammation.
Examples include:- Redensyl, Procapil, Anagain, Caffeine, ChronoShen Night SP, etc.
- Brand formulations: Hairiline, Kopexil, Saw Palmetto Extract, among others These serums may help support topical minoxidil therapy or serve as alternatives in mild cases.
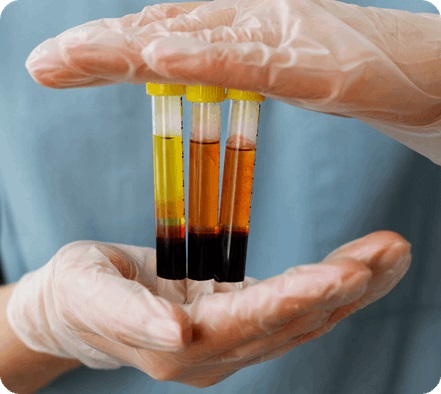
- Injectable Therapies
Minimally invasive treatments can boost localized hair regrowth by stimulating the scalp directly:- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy: Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is a regenerative treatment that involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp. These platelets release growth factors that help stimulate dormant hair follicles, improve blood supply, and support natural hair regrowth. PRP is commonly used for female pattern hair loss and telogen effluvium, often showing visible improvement over a series of sessions.
- Growth Factor Concentrate (GFC): A more advanced, concentrated injectable
treatment.
These are administered by dermatologists and typically done in a series of sessions.
- Topical Minoxidil (2%)
Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for female pattern baldness- Promotes blood flow and prolongs the growth phase of hair follicles.
- Applied once or twice daily to affected scalp areas.
- Most effective when started in the early stages of hair thinning
- Hormonal Treatments
These are suitable for patients with hormonal imbalances, such as irregular menstrual cycles, PCOS, or elevated androgens.- Spironolactone (an anti-androgen) helps reduce DHT and slow follicle miniaturization.
- Oral contraceptives may help balance hormonal fluctuations.
- Prescribed after assessment of hormonal and metabolic profile.
- Stress Management
Since stress is a major trigger for telogen effluvium, managing it effectively is a core part of treatment.- Techniques include mindfulness meditation, yoga, and prioritizing adequate sleep.
- Regular physical activity and lifestyle balance are also recommended.

Prevention and Hair Care Tips
While it may not be possible to prevent genetic hair loss, the following strategies can help reduce shedding and promote stronger hair:
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and avoid excessive heat styling.
- Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the scalp.
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet.
- Get regular health check-ups to catch underlying issues early.
- Consider early intervention with treatments like minoxidil if hair thinning is noticed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Female
Pattern Baldness and Telogen Effluvium
What is the main difference between female pattern baldness and telogen effluvium?
Female pattern baldness is a genetic and hormonal condition that causes gradual hair thinning, especially at the top of the scalp. In contrast, telogen effluvium is usually triggered by stress, nutritional deficiencies, or medications and leads to sudden, diffuse hair shedding across the entire scalp.
Can female pattern baldness be reversed?
Female pattern baldness is a chronic condition and cannot be completely reversed, but treatments such as minoxidil, hormonal therapy, and nutritional supplementation can slow its progression and promote partial hair regrowth.

How long does telogen effluvium last?
Telogen effluvium is typically temporary and lasts between 3 to 6 months. Once the underlying trigger (e.g., stress, illness, or hormonal changes) is resolved, normal hair growth often resumes.
What is the best treatment for female hair loss?
The most commonly recommended treatment for female hair loss is topical minoxidil, which is FDA-approved. Depending on the cause, additional options may include nutritional supplements, hormonal therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Does stress really cause hair loss in women?
Yes, stress is a major contributor to telogen effluvium. It causes a larger-than-normal number of hair follicles to enter the resting (telogen) phase, resulting in increased shedding.
What vitamins help with hair thinning in women?
Key nutrients that support healthy hair growth include biotin, vitamin D, iron, zinc, and protein. A blood test can help identify deficiencies contributing to hair thinning.
How can I tell if my hair loss is hormonal or stress-related?
Hormonal hair loss (female pattern baldness) is usually gradual and follows a predictable pattern, especially at the crown or parting. Stress-related hair loss (telogen effluvium) tends to be sudden, with excessive shedding and a more diffuse pattern. A dermatologist can perform scalp exams and lab tests to determine the exact cause.
Is hair loss in women permanent?
Female pattern baldness can be permanent if untreated, but many cases respond well to
early intervention. Telogen effluvium is usually temporary and reversible once the underlying cause is addressed.

