Melasma Unmasked: Causes, Symptoms, and Proven Treatments for Clearer
Skin
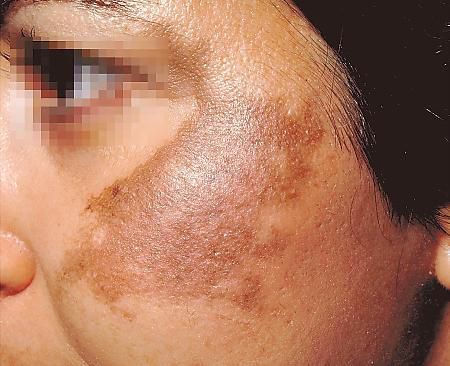
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or gray-brown patches, typically on the face. Often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” melasma affects many women — especially during hormonal changes — but it can also affect men. Though melasma is harmless, it can be emotionally distressing. Fortunately, various treatments and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce its appearance. In this blog, we’ll dive into the causes of melasma, its triggers, treatment options, and prevention tips for long-term skin clarity.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a form of facial pigmentation, caused by overactive melanocytes (pigment- producing cells). It most commonly appears on the:
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Nose bridge
- Chin
- Upper lip
Melasma may also occur on the neck and arms, particularly in sun-exposed areas.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma is primarily caused by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. The most common triggers include:
1. Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) & High-energy Visible Light (HEVL):
- UV & HEVL rays stimulate melanocytes, worsening pigmentation
- Even blue light from screens can aggravate melasma in some people
2. Hormonal Changes:
- Pregnancy: Estrogen and progesterone fluctuations often trigger melasma (known as chloasma)
- Birth Control Pills or Hormone Replacement Therapy
3. Genetics:
- If your family members have melasma, you’re more likely to develop it
4. Skin Irritation:
- Harsh skincare products or cosmetic procedures can trigger inflammation, leading to worsening of pigmentation.
5. Heat Exposure
- Not just sunlight — saunas, cooking heat, or even steamy weather can trigger flare-ups
How to Identify Melasma: Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Melasma typically presents as:
- Symmetrical (equal on both sides) brown or grayish-brown patches.
- Irregular borders.
- No itching or pain.
A dermatologist may use a Woods lamp, dermascope, or skin biopsy to rule out other pigment disorders and come to a definitive diagnosis.
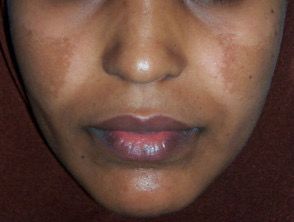
Melasma Treatment Options: What Works Best?
1. Topical Treatments:
- Hydroquinone: Gold standard for melasma, inhibits melanin production.
- Tretinoin: Often combined with hydroquinone in triple therapy.
- Azelaic Acid: Reduces pigmentation with minimal irritation.
- Kojic Acid, Niacinamide, Vitamin C: Gentle alternatives to hydroquinone.
2. Chemical Peels:
- Glycolic acid, lactic acid, or salicylic acid peels can remove superficial pigmentation.
- Best done under dermatologists’ supervision.
3. Laser & Light Treatments:
- Q-switched lasers, fractional lasers, and Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) can reduce pigmentation.
- These must be used cautiously, as improper use can worsen melasma.
4. Oral Medications:
- Tranexamic Acid (TXA): An emerging treatment shown to reduce melasma by interfering with melanin synthesis.
- Used under close medical guidance.
How to Prevent Melasma and Stop It from Coming Back.
Since melasma tends to recur, prevention is crucial even after treatment:
Use Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen Daily.
- SPF 80+, with UVA/UVB protection.
- Reapply every 2–3 hours, even indoors if near windows or screens.
Wear Physical Sun Protection.
- Wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing.
Avoid Heat Triggers.
- Minimize exposure to saunas, hot yoga, and kitchen heat.
Be Gentle With Skincare.
- Avoid harsh scrubs or exfoliants that could inflame your skin.
Limit Hormonal Triggers if Possible.
- Discuss alternative contraception or hormone therapy options with your doctor.
Melasma Myths Debunked
- Melasma only affects pregnant women..
Truth: While common in pregnancy, melasma affects non-pregnant women and men too. - Melasma goes away on its own..
Truth: It may fade post-pregnancy or with hormone changes, but often persists without treatment. - Tanning helps even skin tone..
Truth: Tanning worsens melasma and leads to long-term pigmentation issues.
Final Thoughts: Managing Melasma for Long-Term Skin Health.
Melasma can be stubborn, but it’s not untreatable. With a combination of sun protection, targeted skincare, medical treatments, and patience, you can significantly reduce pigmentation and restore your skin’s natural clarity. Consistency is key — and working with a dermatologist ensures you get a plan tailored to your skin type and triggers.